What is SAML 2.0
SAML is a standard that addresses web-browser single sign-on (SSO). SAML 2.0 is an XML-based protocol that uses security tokens containing assertions to pass information about a principal (usually an end user) between an Identity Provider and a Service Provider.
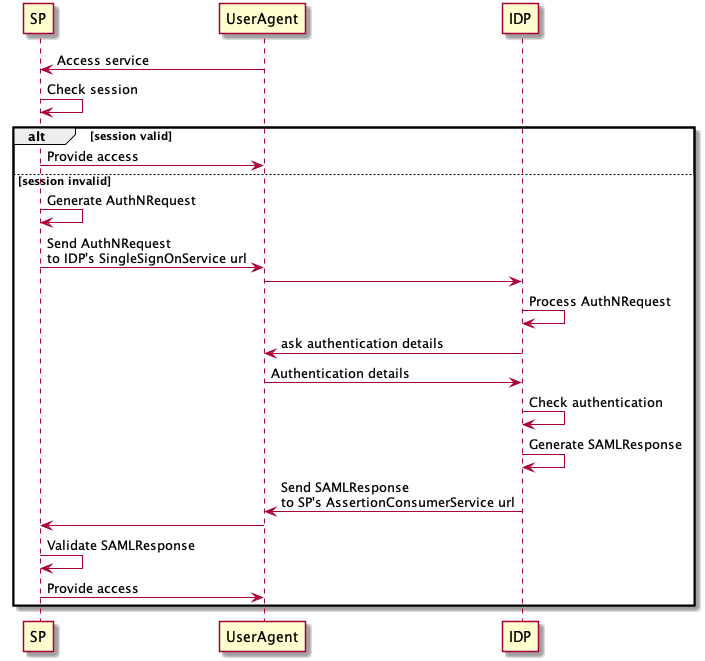
The SAML flow is show in the diagram below
The user via the UserAgent (e.g Browser) tries to access the SP
The SP checks the current authentication session of the user and:
If the user still has a valid session provides the user access to the service
If the user does not have a valid session, it will generate a AuthNRequest and redirects the user to the IDP’s SingleSignOnService url
The IDP checks the AuthNRequest and if valid ask the UserAgent to provide authentication details
The UserAgent provided the authentication details to the IDP.
The IDP checks the user credentials and if valid generates a SAMLResponse containing a SAML Assertion about the user attributes.
The IDP send the SAMLResponse (through the UserAgent) to the AssertionConsumerService url of the SP.
The SP validates the SAML Response and assertions and if valid provides the user access to the service
Integration
For SAML Integration the Service Provider and the Identity Provider first need to exchange their endpoints and signing-certificates with each other. Usually this is done by exchanging a SAML Metadata document. The metadata of Audkenni can be downloaded here. An example of the metadata document that a service needs to provide can de downloaded here
Providing information about the Relaying Party
If the Service Provider is actually also an IDP itself receiving request from other SP’s. Audkenni Mandates that this information is provided in the AuthnRequest